Email frauds by using either real or impersonated email accounts have inflicted businesses with heavy financial and reputational losses. As organizations and security vendors work tirelessly to strengthen their online security strategies and educate their employees regarding new business email scams, hackers continue to develop their email scamming techniques and pose tough security challenges.
-
The yearly FBI cybercrime report 2020
(Source:https://www.ic3.gov/Media/PDF/AnnualReport/2020_IC3Report.pdf) reveals that Business Email Compromise(BEC) resulted in the most financial damage standing at a huge amount of $1.8 billion in confirmed losses, which is about 37% of the losses associated with all the cybercrime losses. The data from 2018-2020 below makes this fact evident.
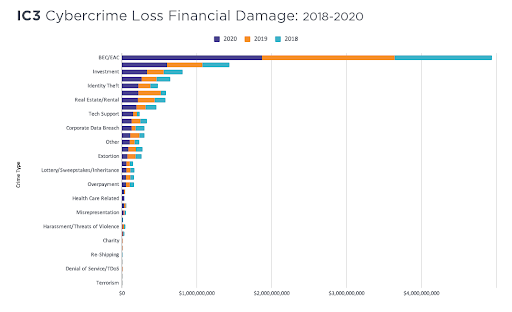
(Source: https://www.agari.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/chart01-IC3-cybercrime-losses.png )
So, here for your benefit, we bring together various types of BEC that are hitting the enterprises and hackers’ various techniques. Then we further focus on essential security tips that organizations should incorporate to educate their employees to prevent such attacks. But before that, let us first try to understand the basics of a Business Email Compromise and how it works.
-
Understanding Business Email Compromise
Business email compromise (BEC) or the man-in-the-email fraud is financially driven. It mainly targets the unwary principal heads of the businesses and their employees and tricks them into transferring sensitive data or money into fake accounts. These attacks are carried out using various techniques such as social engineering, impersonation, etc.
To get the targeted plan executed right through the business people themselves by tricking them into following the steps that help attackers defraud companies off huge sums of money or steal sensitive data.
Unfortunately, BEC comes as a big challenge when it comes to prevention as no routine processes of threat detection such as analyzing email links or headers or even metadata seem to be effective in catching the techniques used by these attacks.
For working towards robust email security, it is important to protect all the communication between the user’s web browser and the webserver. For this, you need to buy and install an SSL certificate.
Securing your website with even a little investment like getting a cost-effective cheap PositiveSSL or RapidSSL cert to secure your website. The connection can provide complete security for all the data in transit by encrypting them and shifting the website’s protocol to secure HTTPS (HTTP + SSL = HTTPS.)
-
Step By Step Working Of BEC Attack
While the attackers’ capability, the scale at which it is working, its research, its use of technology, and its ultimate goal together are a few deciding factors that will ultimately determine the complexity of the technique adapted to carry out the BEC attack. But a typical BEC attack can be broadly broken up into the following stages listed below.
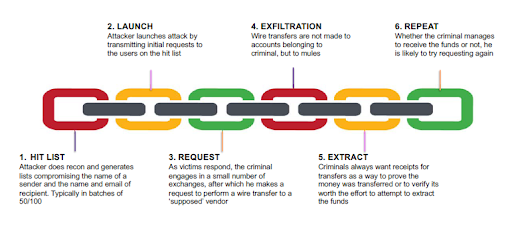
(Source: https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/media/images/Figure_2_BEC.original.png )
-
Target Identification And Profiling
The BEC attackers at the onset identify their suitable targets or create a hit list that includes employees or executives of the organization who are authorized to make online transactions for their enterprise.
Next, they build the company and executive profiles, collect information on their social media platforms, the contact information on various websites to conduct thorough research, and then select their target.
-
Set The BEC Attack Rolling
The BEC attackers start initiating requests to the set target using different methods like spear-phishing emails, spoofing email addresses, creating fake similar-looking domains, using impersonations, and hacking into the executive’s email account in authority.
-
BEC Attack Execution
After the victim starts to respond, it may take attackers one or more email exchanges spread over a period to make the victim believe its legitimacy and win trust depending upon the persuasion power and techniques used.
Finally, using some urgent requests in the email, attackers get the victim tricked into getting a financial transfer done into their fraud accounts or make them share confidential data with the perpetrators.
-
Final Payments Dispersal
If the attackers are successful in their motives, this is the last step to earn monetary profits or crucial data access. After receiving money, these hackers have a well-organized network and system to distribute the amount by laundering and transferring it to multiple accounts quickly. This makes it very difficult to trace and recover the illegal amount transferred.
-
Common Types of BEC Attacks
The most common BEC attacks can be broadly classified as follows:
-
CEO Impersonation
Here, attackers impersonate the executive head of the enterprise and send emails to the authorized employee to make transactions, requesting to transfer money to an illegal account held by the hackers.
-
Lawyer Fraud
This scam is executed when the attacker impersonates a lawyer or a legal representative and communicates with employees working at lower positions who wouldn’t be knowledgeable enough to question the authenticity of the urgent request posted.
-
Data Compromise
This attack is carried out by basically targeting HR personnel to steal the personal and sensitive information of the company’s senior executives and CEO. The attackers aim to use this information to carry out frauds like CEO fraud. The 2016 BEC attack against social media firm Snapchat resulted in its employees’ major sensitive data breach.
-
Email Account Compromise
Here, an email account of an employee is hacked and is then misused to request payments to the vendor further. The payments thus sent to the vendor are deposited in the account held by the hackers.
-
Vendor Email Scam
Attackers’ target companies worked with foreign suppliers by presenting a fake invoice and requesting payments against it. The attackers pose as suppliers and thus request payments into fake accounts. e.g., The Rimasauskas scam against Google and Facebook, which incurred around $121 million losses.
-
How To Protect Your Business From BEC Attacks
 (Source: https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRg_v5J75vHDecWF-9_6GEiwqMsGwmb6MAwrg&usqp=CAU )
(Source: https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRg_v5J75vHDecWF-9_6GEiwqMsGwmb6MAwrg&usqp=CAU )
Here are some of the best security practices that must be incorporated into the security strategy to minimize the BEC attacks and their impacts.
-
Enable MFA Authentication
Enabling Multi-Function Authentication has become essential, especially with a remote workforce, to protect employees’ accounts at a high risk of BEC attacks like CEOs of the company, employees directly responsible for financial transactions, administrators, and human resources. Additionally, any urgent payment requests in an email from vendors must be first checked by contacting him directly before any wire transfers.
-
Take An Audit OF Email Security Capabilities
The delivery has increased due to dependency on a cloud with improved security features in place of Secure Email Gateways (SEG) for email. With organizations shifting to remote working, there is a compulsive need to get your email security audit done. In addition, total dependency on native email security must be evaluated to highlight any weak links in the email security procedures.
Accordingly, the organization should adopt the recommendations from various configuration analyzers available in the market, like the free Office 365 Configuration Analyzer, for appropriate email security configuration procedures and improve email security posture.
-
Pay Attention To These Warning Signs
The format of BEC attacks is that it tries to create urgency and force the victims to act before it can start reasoning things out. Hence, it is really important to train your employees to be aware and look for the signs that tell them that they may have been targeted by Business Email Compromise.
Always investigate any deadline issued at short notice involving crucial data or money transactions.
Look for unusual purchase requests, even if it is from some senior executive that you must trust.
Watch out for emails that carry any new deposit account details from employees or vendors for invoice payments. An MFA must be put in place for vendor verification.
Unusual grammatical mistakes from the sender you know can again be a pointer towards a spoofed email. Again, you can separately confirm this by separately sending a message instead of replying to it.
In conclusion:
Organizations need to create awareness among their employees and arrange regular security drills to train them against SEC frauds. In addition, you need to continuously work with your security vendors and security teams to evolve new processes and security tools to keep up with the growing Business Email Compromise threat.


 (Source:
(Source: 



